OIL AND GAS
The oil and gas industry relies heavily on specialized equipment and vehicles, as their operations are complex and require precise, reliable tools.
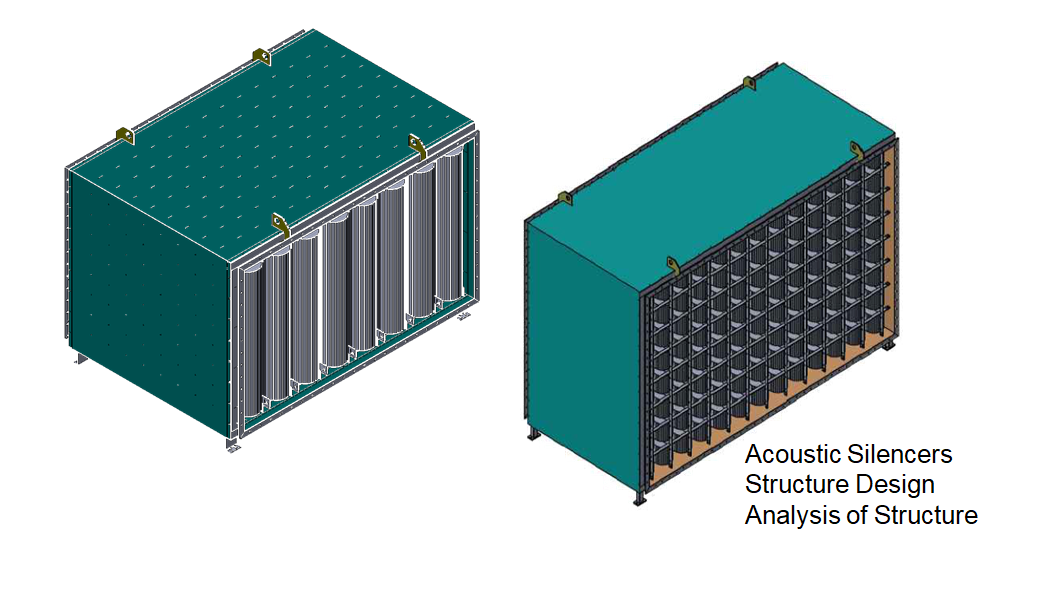
Acoustic Enclosures
Acoustic enclosures are structures designed to reduce noise levels by isolating or absorbing sound produced by equipment, machinery, or processes in industrial, commercial, and residential environments.
Exhaust System and Silencers
Exhaust Manifold: Collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders.
Catalytic Converter: Reduces harmful emissions by converting pollutants into less harmful gases.
Tailpipe: The final part of the exhaust system, where gases exit the vehicle.
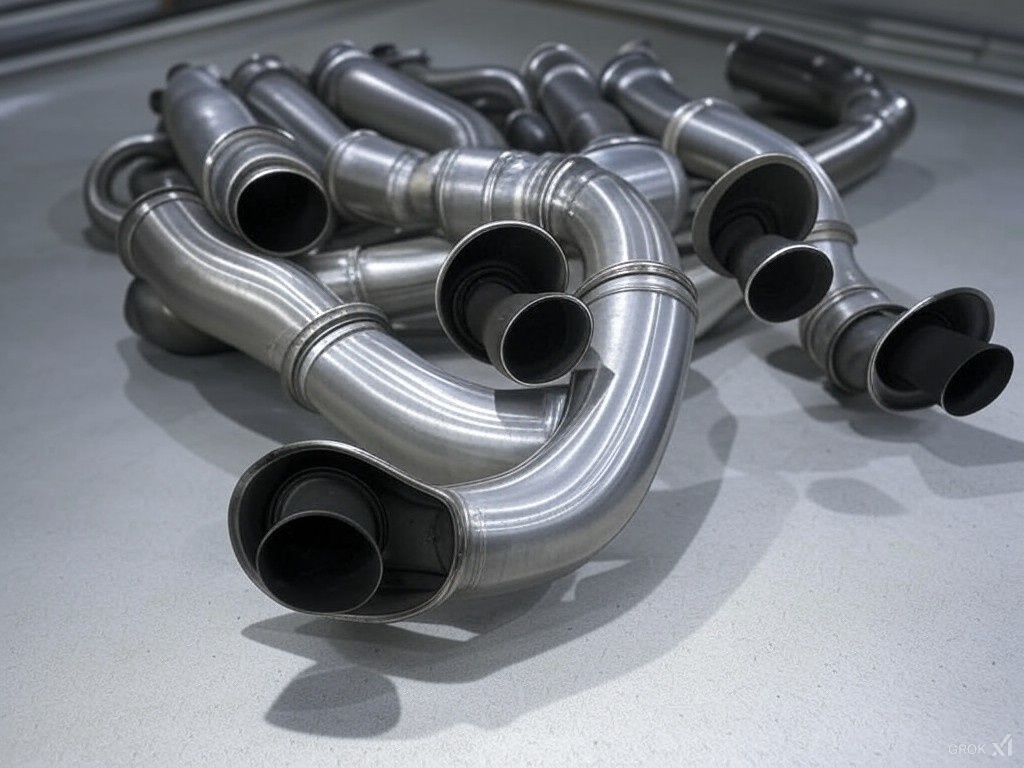
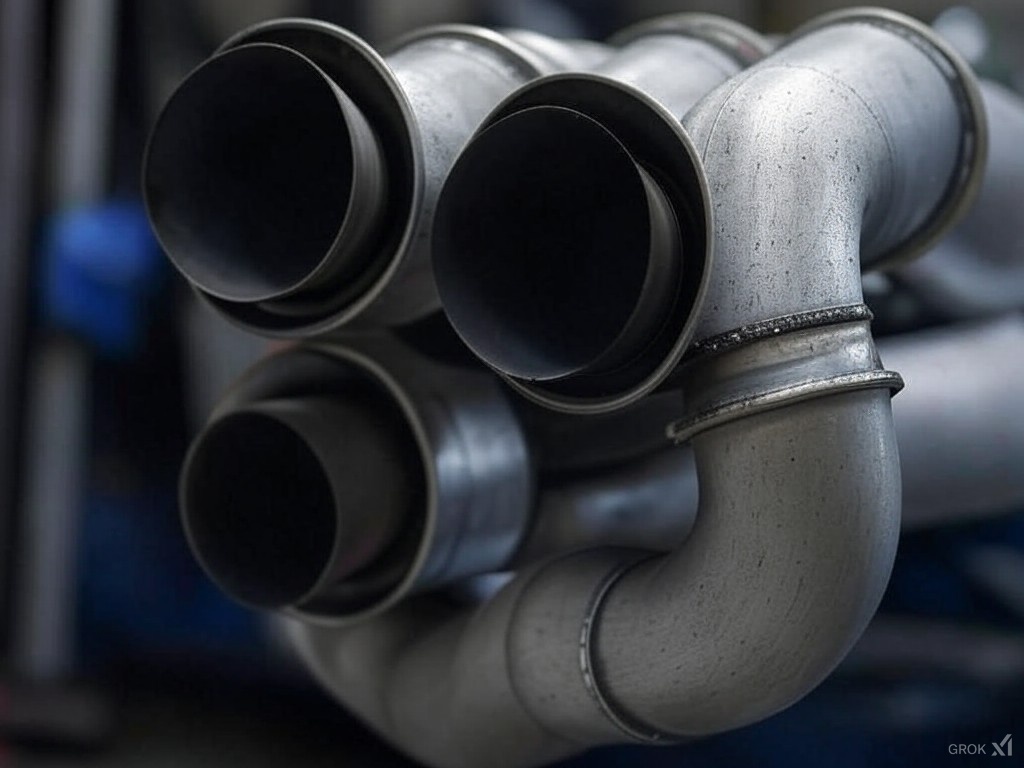
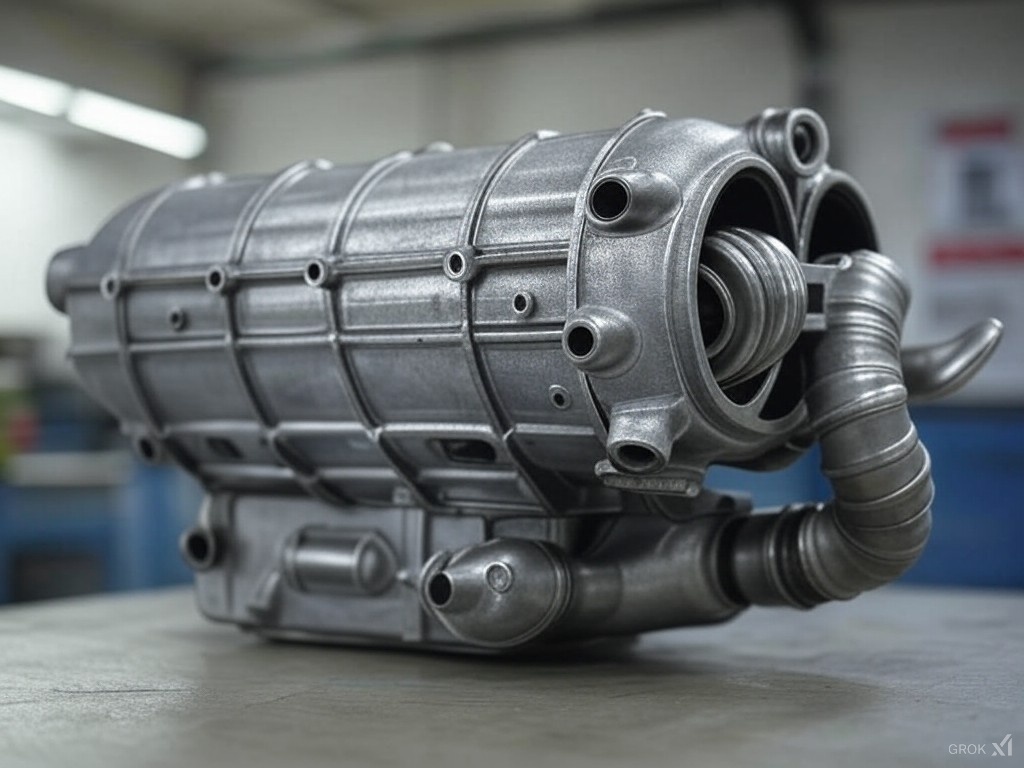



Silencer (Muffler) Design and Function
The silencer (also known as a muffler) is designed to reduce the noise emitted by the exhaust system. It typically works by reflecting sound waves inside a chamber with perforated tubes or baffles, which cancel out the sound. The exhaust gases and the sound waves enter through the center tube. They bounce off the back wall of the muffler and are reflected through a hole into the main body of the muffler. They pass through a set of holes into another chamber, where they turn and go out the last pipe and leave the muffler.
Construction: Mufflers are typically made of stainless steel or aluminized steel to resist corrosion from heat and chemicals. Inside, they contain a combination of resonating chambers, baffles, and sound-absorbing materials like fiberglass or steel wool.
Absorptive Silencers: Use sound-absorbing materials to reduce noise directly.
Fiberglass is the most commonly used material inside of traditional mufflers.
